Many people get tattoos that for one reason or the other, they no longer desire to have. The only current option to erase permanent tattoos is laser tattoo removal. The process of removing tattoos by laser therapy is long, painful, expensive, and in about 5% of cases complications can arise. However, a faster, easier, and cheaper method of tattoo removal may soon be on the market. Most recently, a scientist by the name of Alec Falkenham came up with the idea for an investigational tattoo removal cream, when he was a pathology PhD student at Dalhousie University in Halifax, Nova Scotia. As of 2016, the cream is being developed by Cipher Pharmaceuticals Inc. for commercial use.
Tattoo Removal Cream
Bisphosphonate Liposomal Tattoo Removal is a topical cream intended to remove or reduce the appearance of tattoos. It is designed to be used alone or as an adjuvant to hasten the process of laser tattoo removal. It is proposed that the cream would require once a week application, and remove the tattoo in as little as a couple of months.
Complications of Laser Tatttoo Removal
Immediate
- Pain
- Blisters and crusting
- Pinpoint hemmorage
- Urticaria
Delayed
- Pruritic Papules and nodules
- Scaly plaques
- Paradoxical darkening (hyperpigmentation)
- Texture change and Scarring (temporary or permanent
How and why does it work?
When a person receives a tattoo, the ink that is deposited into the skin undergoes phagocytosis by white blood cells known as macrophages. Some of the infiltrating macrophage engulf ink particles and carries them away to the lymphatic system, to be cleared from the body. Other macrophages remain within the skin at the application site, where they sequester the ink, and are responsible for the permanency of tattoos. Over time, this process continues, with new macrophage infiltrating the tattooed skin, and removing both ink and old macrophages that had sequestered ink. This is the reason, why tattoos naturally fade.
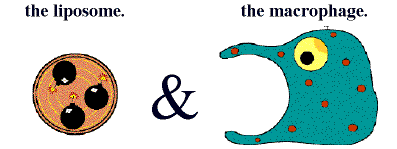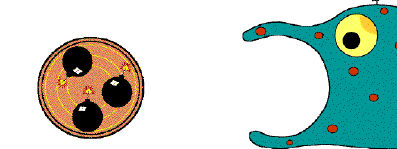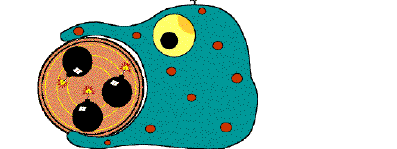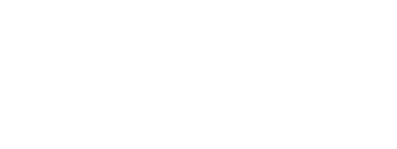
The premise behind the tattoo removal cream capitalizes on this natural process. The cream employs Bisphosphonate, a drug that is cytotoxic to macrophages. It kills the macrophages within the tattoo site, which causes them to release the ink they have encapsulated. This results in the recruitment of new macrophage to the site, which removes both dead macrophages and ink. Bisphosphonate Liposomal Tattoo Removal hastens the body’s natural tattoo fading process.
Liposomal Bisphosphonate
Bisphosphonate
Liposomal Bisphosphonate is the encapsulation of the drug bisphosphonate in liposomes. Bisphosphonate has traditionally been used to treat bone disease such as osteoporosis, hypercalcemia, and Paget’s disease, by inhibiting bone resorption by osteoclasts. Osteoclasts are specialized macrophages that reside in bone.
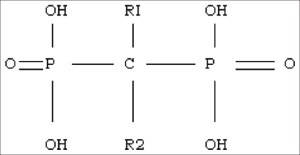
There are two types of Bisphosphonate, non-nitrogen containing and nitrogen containing. Non-nitrogen containing bisphosphonates are prodrugs that are converted to their active form when metabolized by macrophage. The metabolite of non-nitrogen bisphosphonates are analogs of ATP (adenosine tri-phosphate) that are not able to be hydrolyzed and are therefore inactive and toxic to the cell. ATP is the store-house of energy inside of cells. When it is hydrolyzed it releases this energy that is used by the cell for various processes including survival. By blocking the recycling of ATP to ADP (adenosine di-phosphate) and back, cells undergo direct apoptosis resulting in cell death. Nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates, however function differently. They interfere with one or more steps in the Mevalonate pathway, responsible for cholesterol synthesis. Mevalonate is an intermediary compound that is transformed into isoprenoid lipids, necessary for postranslational modificiations that regulate cellular processes such as proliferation, motility, and survival. Nitrogen-containing Bisphosphonates generally cause cell death by indirect apoptosis, but recent studies show that they are also involved with the production of toxic ATP analogues and can cause direct apoptosis in macrophages.
Liposomes
Liposomes are artificial lipid bilayers composed of self assembling lipids made up of cholesterol and phospholipids, with an aqueous inner compartment. Liposomes are able to carry hydrophobic drugs within their bilayer, or hydrophobic drugs within their aqueous center.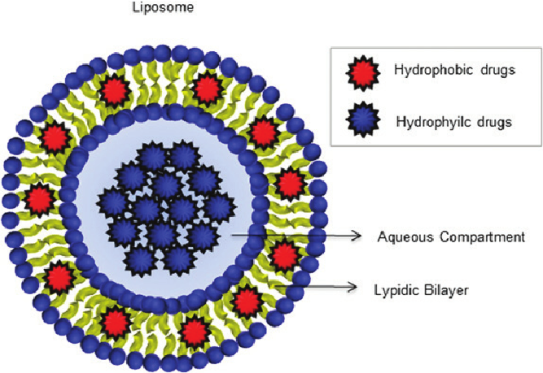
Liposomes can activate the compliment system, triggering the recruitment of macrophages in the immune system to clear pathogens, foreign body’s like ink particles, and damaged cells. Liposomal encapsulation of bisphosphonate is advantageous because liposomes are readily absorbed by phagocytic cell. Macrophage contain lypsases that degrade the lysosome lipid bilayer causing the release of bisphosphate dissolved within the aqueous compartment into the cell. Additionally,liposomal encapsulation of bisphosphonate is reportedly 20 to 1000 times more effective at inhibiting macrophage than free bisphosphonate.
Safety & Efficacy
Bisphosphonate Liposomal Tattoo Removal cream reportedly does not cause damage to regularskin cells, as the cytotoxicity of bisphosphonate is specific to macrophage cells. Bisphosphonate has been routinely shown in various studies to cause apoptosis in phagocytic cells both in vitro (cell culture) and in vivo (live whole animal). In addition to being used for the treatment of bone disease, bisphosphonate has also been investigated for use in treating rheumatoid arthritis, cancers, and atherosclerosis.
Traditionally, Bisphosphonate is administered either orally or intravenously. Frequent, long-term administrations of Bisphosphonate via these routes are associated with renal toxicity, osteonecrosis of the jaw, hypocalcemia, and gastrointestinal tract problems, such as mucosal irritation, esophagitis, and gastric ulceration. However Bisphosphonate Liposomal Tattoo Removal cream is applied topically, and used infrequently for a short duration of time.
Topical application to the ears of mice and pig in pre-clinical studies were effective at removing ink in just two applications. Some reservation needs to be made in terms of efficacy when it come to the mouse ear, as it has fewer layers than human skin, the drug may absorb more readily into the dermis. Also fewer layers of skin to clear ink from means faster removal. However, pig skin is analogous to human skin , and thus these data are still appreciable.
Summary
The exact formulation of the tattoo fading lotion is not known, as it is still under development and patent, and has not yet been FDA approved. However, it is reported to not cause any cutaneous side effects, such as, dry skin or irritation. Preclinical testing on mice and pig ears showed that the cream does not cause irritation or inflammation, which is consistent with bisphophonates, as they are anti-inflammatory agents. Bisphosphonates inhibit the release of various cytokines involved in inflammation, such as, interleukins, tumor-necrosis factor – alpha, and nitrogen oxide, and this should offset the inflammation triggered by liposomes due to the activation of the compliment system.
Combining bisphosphonate phagocyte toxicity with the compliment system activation of liposomes strategically accomplishes the task of accelerationg the natural tattoo fading process by the body. Ink containing macrophages are killed, while new macrophages are recruited to tattooed skin, to remove both dead cells and ink, while sequestering more ink. Bisphosphonate Liposomal Tatttoo Removal cream accelerates this process.
Reference
Aderibigbe B. Aderibigbe I. and Papoola P., 2017. Design and Biological Evaluation of Delivery Systems Containing Bisphosphonates. Pharmaceutics Vol 9 (2).
Khunger N., Molpariya A., and Khunger A., 2015.Complications of Tattoos and Tattoo Removal: Stop and Think Before you ink. J Cutan Aesthet Surg Jan-Mar Vol 8(1) pg 30-36
Monkkonen H., Rogers M.J., Makkonen N., Niva S., Auriola S., Monkkonen J., 2001.The cellular uptake and metabolism of clodronate in RAW 264 macrophages. Pharmaceutical Research, Vol. 18 No.11 pg 1550
Lewieck M.E., 2011. Safety of Long-Term BisphosphonateTherapy for the Management of Osteoporosis. Drugs Vol 71 No. 6 pg 791-814.
Anonymous, 2008. Adverse-effect profiles of bisphosphonate ar largely determined by their route of administration. Drug & Therapy Perspectives. Vol 24 No 7 pg 23.
Staff writer. Student Creates Tattoo Removal Cream. RTTNew, Williamsville 19 Feb 2015.
Mejia Paula. Tattoo Regret? A Topical Removal Cream May Help. Newsweek, Global ed., New York, 13 Mar 2015.

Amazing and informative article, really going into depth to explain how this really could work. Is there theoretically any reason why this wouldn’t work for other dermal pigment? Such as dermal hyperpigmentation? From my understanding this is also macrophages, just filled with melanocytes rather than ink – so wouldn’t this be equally effective for dermal pigmentary disorders? I find it odd how it only focuses on tattoos, without looking at this avenue.
LikeLike
That’s interesting, perhaps it could be adapted for that also. Good thinking!
LikeLike
The melanin is in melanosomes in the macrophages and not in melanocytes.
LikeLike
This is a good article explaining the mechanism of macrophages and their role in pigment. I agree with the other commenter as I have thought about the creams application in removing hyperpigmentation of the skin.
Liposomal clodronate (the bisphosphate Alec Falkenham’s patent references repeatedly) is actually really easy to purchase from labs around the US as it is used heavily in research in animal models. One could theoretically compound LC with a transdermal topical ointment (e.g. Lipoderm or transdermal pain base) and use themselves as a guinea pig. The patent references a huge range of concentration from .001% to 10%.
Here is a link to the patent
https://www.google.com/patents/WO2015027328A1?cl=en&dq=tattoo+removal+cream&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjq1M-BqJfZAhUBwGMKHf-PB5IQ6AEINzAC
LikeLike
Yes, great article. That is exactly what a friend of mine and I were thinking since 2 years what this lady before wrote about dermal pigmentation. The company who bought the cream was asked by her and they are just stating, that it is only meant for tattoo removal. But I believe it could work on dermal pigmentation too. What do you think? It is non-nitrogen containing BP or nitrogen containing BP which is used in the cream? what kind of lotion could it be? It can’t be something to fancy as liposomal lotion used for this cream. It was a student who was discovering this by chance. So look around what has been used in hospitals, were he worked. This facts put together should help. I am also desperate having this awful dermal hyper pigmentation. So please comment Stacia Nicholson. I would really do anything to get rid of it. you can also send me a private message. Thank you.
LikeLike
Good web site! I really love how it is simple on my eyes and the data are well written. I’m wondering how I could be notified whenever a new post has been made. I’ve subscribed to your RSS feed which must do the trick! Have a great day!
LikeLike